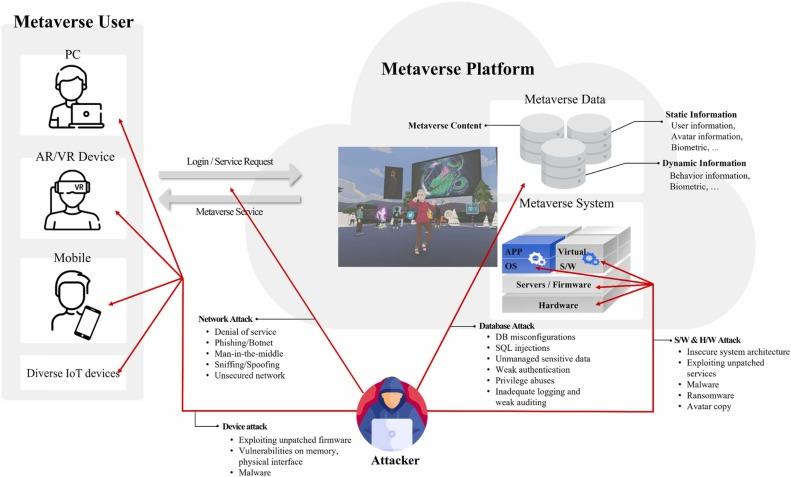
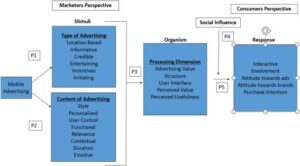
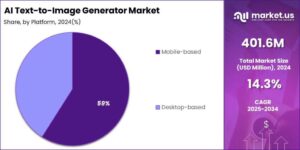
When encountering the error message ”The %%topic%% placeholder is empty,” users face a common technical issue in content management systems and template-based applications. This error typically occurs when a system expects a topic variable to be populated but receives no data, resulting in a failed attempt to generate an appropriate article title. The placeholder syntax, denoted by percentage signs, is designed to be replaced with actual content during processing, making its emptiness a critical error that requires attention. The human brain’s remarkable capacity for pattern recognition extends far beyond simple visual identification. This intricate ability encompasses multiple sensory modalities, enabling us to detect regularities in sound, touch, and even abstract concepts. Pattern recognition serves as a fundamental cognitive process that has been crucial for human survival and development throughout evolution.
When encountering new information, our brains automatically search for familiar patterns within stored memories and experiences. This process occurs through complex neural networks that analyze incoming data and compare it with existing knowledge. The brain’s pattern recognition system operates on both conscious and unconscious levels, allowing for rapid processing of environmental stimuli and appropriate response generation.
Scientists have identified specific brain regions that play crucial roles in pattern recognition. The temporal lobe processes visual patterns, while the parietal lobe integrates sensory information from different sources. The prefrontal cortex handles more abstract pattern recognition tasks, such as identifying relationships between concepts or recognizing social behavior patterns.
Pattern recognition manifests in various cognitive functions. In language acquisition, children recognize grammatical patterns without explicit instruction. Musicians identify harmonic patterns within compositions, enabling them to predict and create melodic progressions. Mathematics relies heavily on pattern recognition for problem-solving and theorem development.
The brain’s pattern recognition capabilities also influence decision-making processes. When faced with new situations, we unconsciously search for similar past experiences to guide our actions. This mechanism helps us navigate social interactions, predict outcomes, and adapt to changing environments. However, this same system can sometimes lead to cognitive biases when patterns are incorrectly identified or overgeneralized.
Advanced artificial intelligence systems attempt to replicate human pattern recognition abilities through machine learning algorithms. These systems process vast amounts of data to identify patterns and make predictions, yet they still fall short of the human brain’s sophistication in handling novel or ambiguous situations.
Pattern recognition abilities vary among individuals and can be enhanced through practice and exposure. Professional analysts, for instance, develop superior pattern recognition skills within their specific domains. Chess masters recognize complex board positions from previous games, allowing them to make strategic decisions rapidly.
Understanding pattern recognition’s role in cognitive function has important implications for education, technology development, and therapeutic interventions. Educational methods that leverage natural pattern recognition abilities can enhance learning outcomes. Cognitive rehabilitation programs focus on strengthening pattern recognition skills in patients with brain injuries or neurological conditions.
The brain’s pattern recognition system continues to evolve throughout life, adapting to new experiences and challenges. This plasticity enables continued learning and skill development, demonstrating the remarkable flexibility of human cognitive abilities. Research in this field provides insights into both human consciousness and the development of more sophisticated artificial intelligence systems.