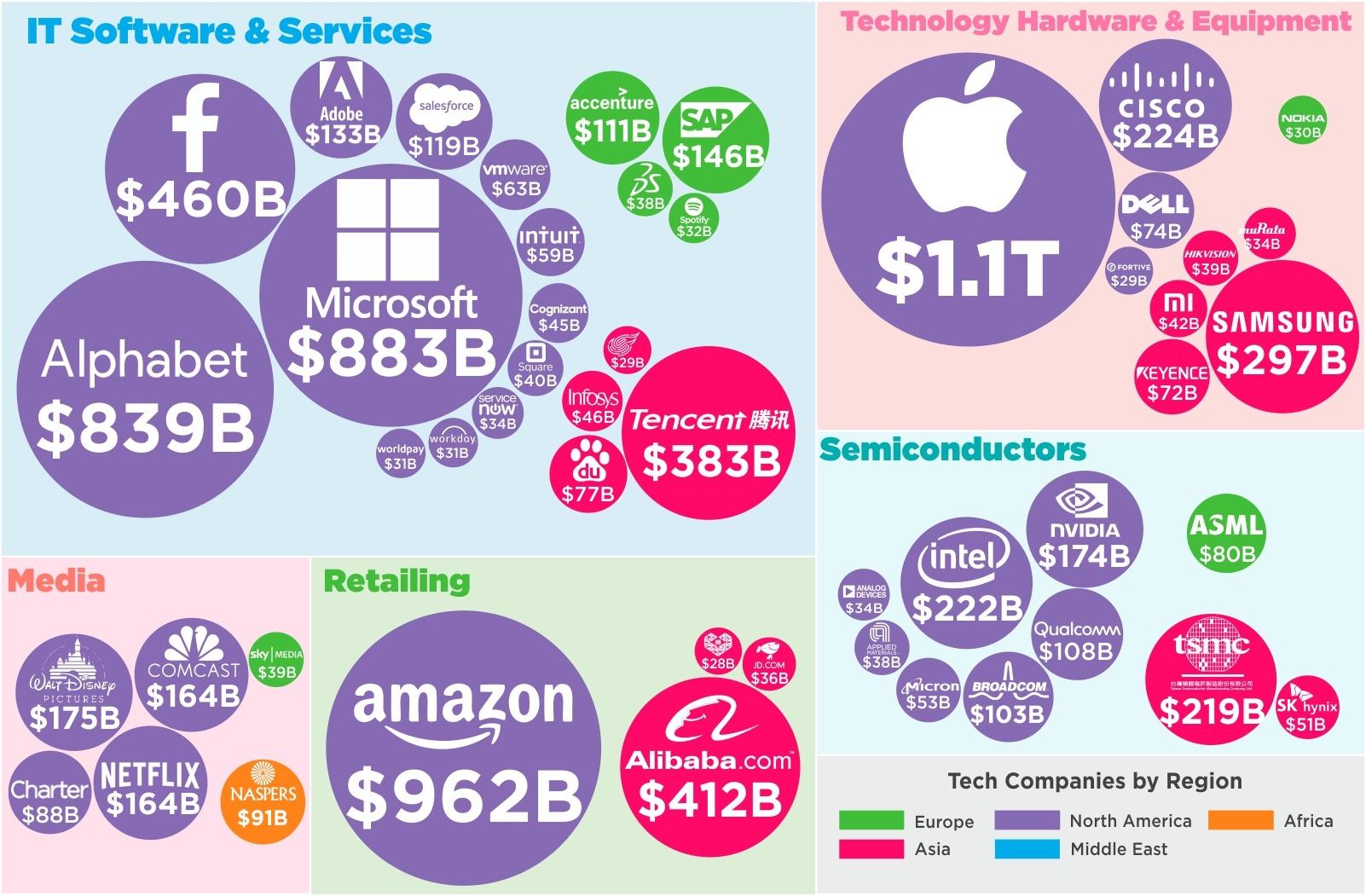
The landscape of global technology has been dominated by a select group of corporations that have fundamentally transformed how we live, work, and interact. These tech giants, through innovation and market expansion, have achieved unprecedented market capitalizations, becoming some of the world’s most valuable companies. From cloud computing and e-commerce to social media and consumer electronics, these industry leaders have established themselves as pillars of the modern digital economy, influencing technological advancement and setting industry standards across multiple sectors. The digital landscape has revolutionized how businesses operate, making data security a paramount concern. Organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information, maintain customer trust, and ensure business continuity. Multi-factor authentication serves as a crucial defense mechanism, requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods before gaining access to systems.
Regular software updates and patch management help address vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit. Companies should establish clear protocols for updating all devices, applications, and systems within their network. Employee training programs play a vital role in creating a security-conscious workplace culture, as human error remains a significant factor in data breaches.
Encrypted communication channels protect data transmission between parties, making it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to intercept or decipher sensitive information. Implementation of end-to-end encryption for emails, messaging systems, and file transfers adds an essential layer of security to daily operations.
Network segmentation limits the potential damage of security breaches by dividing networks into smaller, isolated sections. This approach contains threats within specific segments, preventing them from spreading throughout the entire system. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify weaknesses in the infrastructure before malicious actors can exploit them.
Data backup strategies ensure business continuity in case of ransomware attacks or system failures. Organizations should maintain multiple copies of critical data, including off-site backups and cloud storage solutions. Incident response plans outline specific procedures for addressing security breaches, minimizing damage, and restoring normal operations quickly.
Zero-trust architecture assumes no user or system can be automatically trusted, requiring verification for all access requests regardless of location or network connection. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and lateral movement within networks.
Mobile device management becomes increasingly important as remote work continues to grow. Organizations must implement policies governing the use of personal devices for work purposes and ensure proper security measures are in place for company-owned devices.
Cloud security requires special attention as businesses migrate more operations to cloud platforms. Understanding shared responsibility models and implementing appropriate security controls helps protect data stored in cloud environments. Regular monitoring and logging of system activities help detect suspicious behavior and potential security threats early.
Access control systems should follow the principle of least privilege, granting users only the permissions necessary to perform their job functions. Regular access reviews ensure terminated employees no longer have system access and current employees maintain appropriate permission levels.
Compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws requires ongoing attention and documentation. Organizations must stay informed about changing requirements and adjust their security measures accordingly. Third-party risk management helps ensure vendors and partners maintain adequate security standards when handling company data.
Integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning enhances threat detection and response capabilities, allowing systems to identify and react to potential security incidents more quickly than traditional methods.