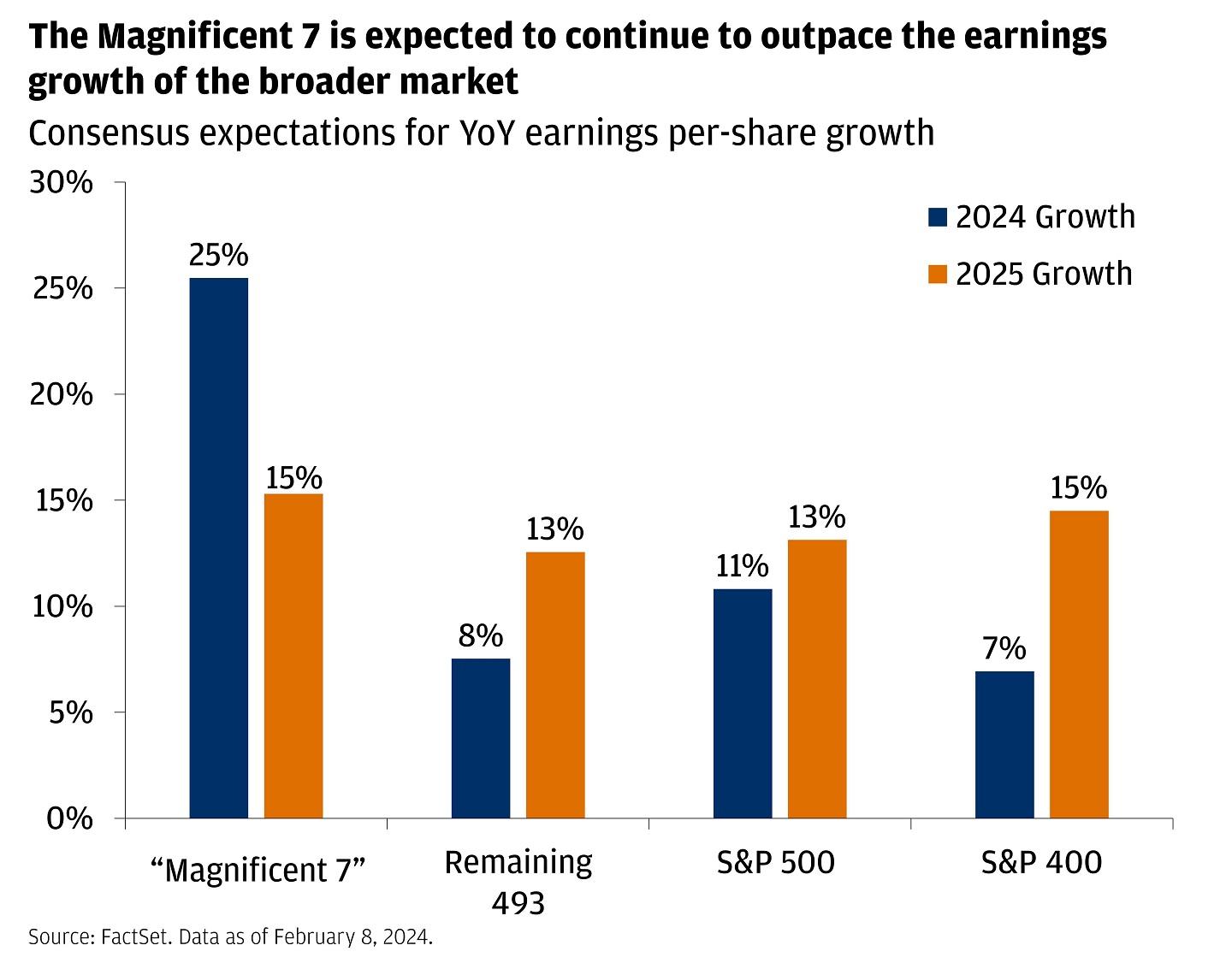
The technology sector’s remarkable surge in early 2024 has fundamentally altered the landscape of market leadership, with artificial intelligence-driven gains propelling select tech giants to unprecedented valuations. As companies like Microsoft, Nvidia, and Meta continue their upward trajectory, their expanding market capitalization is reshaping major indices and challenging traditional market dynamics. This shift reflects both the growing influence of AI technologies and investors’ renewed confidence in tech stocks, marking a significant departure from the sector’s challenges in 2022. The process of urbanization is reshaping our world at an unprecedented pace, transforming rural landscapes into sprawling metropolitan areas. As cities expand and populations migrate towards urban centers, this fundamental shift brings both opportunities and challenges for societies worldwide. Infrastructure development struggles to keep pace with rapid urban growth, leading to increased pressure on housing, transportation systems, and public services.
Population density in urban areas continues to rise, creating unique social dynamics and economic patterns. High-rise buildings dominate city skylines, while former agricultural lands give way to residential developments and commercial zones. This transformation affects not only the physical landscape but also traditional social structures and cultural practices.
Environmental implications of urbanization manifest through increased energy consumption, waste generation, and air pollution. Cities account for approximately 75% of global carbon emissions, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable urban planning. Green spaces diminish as concrete structures multiply, affecting local ecosystems and biodiversity.
Economic activities concentrate in urban areas, creating employment opportunities and driving innovation. However, this concentration also leads to income disparities and social segregation. While some urban districts thrive with modern amenities and resources, others struggle with inadequate infrastructure and limited access to basic services.
Housing affordability emerges as a critical challenge in rapidly urbanizing regions. Property values soar in desirable locations, pushing lower-income residents towards peripheral areas. This spatial reorganization affects social mobility and access to opportunities, potentially perpetuating cycles of inequality.
Public transportation systems face mounting pressure to serve expanding urban populations efficiently. Traffic congestion becomes a daily challenge, impacting productivity and quality of life. Smart city initiatives emerge as potential solutions, incorporating technology to optimize urban services and improve resource management.
Healthcare systems adapt to serve dense urban populations, with medical facilities concentrated in city centers. However, accessibility remains uneven, particularly in rapidly growing urban peripheries. Mental health concerns increase due to urban stress factors, including noise pollution and reduced access to natural environments.
Educational institutions cluster in urban areas, offering diverse learning opportunities. However, overcrowded schools in some districts contrast with well-resourced facilities in others, reflecting broader urban inequalities. Digital infrastructure becomes crucial for modern urban education systems.
Cultural dynamics evolve as diverse populations concentrate in urban areas. Traditional community bonds may weaken, while new forms of social interaction emerge. Urban spaces become melting pots of different cultures, fostering innovation but also creating potential for social tension.
Water management and sanitation systems face increasing demands in urban areas. Cities must invest in infrastructure to ensure sustainable water supply and waste management. Climate change adds complexity to these challenges, requiring adaptive urban planning strategies.
Employment patterns shift as cities become centers of service-based economies. Manufacturing activities often relocate to urban peripheries, while central business districts focus on knowledge-based industries. This transformation affects labor markets and skill requirements for urban workforces.