The technology sector is poised for a significant shift in 2025 as emerging companies challenge the long-standing dominance of established tech giants. While corporations like Apple, Google, and Meta have traditionally controlled market dynamics, a new wave of innovative startups and mid-sized companies is gaining momentum, armed with disruptive technologies and agile business models. This evolving landscape presents both opportunities and risks for investors, consumers, and industry stakeholders as the battle for market share intensifies. Virtual reality (VR) technology has revolutionized the way we experience digital content, transforming various sectors from gaming and entertainment to education and healthcare. This immersive technology creates three-dimensional environments that users can explore and interact with, offering unprecedented levels of engagement and presence.
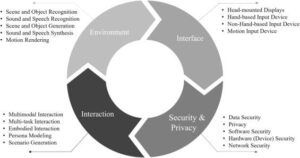
The core components of VR systems include head-mounted displays (HMDs), motion sensors, and controllers. These devices work in tandem to track user movements and translate them into corresponding actions within the virtual space. Advanced VR systems incorporate haptic feedback, enabling users to feel virtual objects and experience tactile sensations.
The applications of VR extend far beyond entertainment. In healthcare, medical professionals utilize VR for surgical training, allowing them to practice complex procedures without risk. Mental health practitioners employ VR exposure therapy to treat phobias and anxiety disorders by creating controlled environments where patients can confront their fears safely.
Educational institutions have embraced VR as a powerful learning tool. Students can take virtual field trips to historical sites, explore anatomical structures in detail, or conduct dangerous experiments in safe, simulated environments. This hands-on approach enhances comprehension and retention of complex concepts.
In the business sector, VR facilitates remote collaboration, virtual prototyping, and architectural visualization. Companies can conduct virtual meetings where participants feel physically present, reducing travel costs and improving communication. Architects and designers use VR to walk clients through building designs before construction begins.
The real estate industry has adopted VR for virtual property tours, enabling potential buyers to explore homes from anywhere in the world. This technology has become particularly valuable during periods when physical viewings are impractical or impossible.
Military and law enforcement agencies utilize VR for combat training and crisis response scenarios. These simulations provide realistic experiences without the associated risks, helping personnel develop critical decision-making skills under pressure.
The entertainment sector continues to push VR boundaries with immersive gaming experiences and interactive storytelling. Users can step into their favorite games or experience narratives from first-person perspectives, creating unprecedented levels of engagement.
Despite its advantages, VR technology faces challenges including motion sickness, hardware limitations, and content development costs. However, ongoing technological advancements are addressing these issues through improved displays, reduced latency, and more sophisticated tracking systems.
The social implications of VR are significant, with platforms emerging that enable users to interact in virtual spaces, attend concerts, or participate in shared experiences. This technology has the potential to reshape how we connect, learn, work, and entertain ourselves.
As hardware becomes more affordable and content creation tools more accessible, VR adoption continues to grow. The technology’s ability to create immersive, interactive experiences makes it a powerful tool for various applications, fundamentally changing how we interact with digital content and each other.