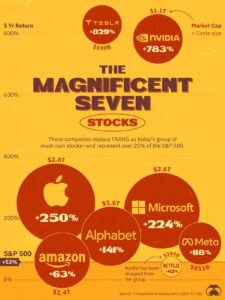
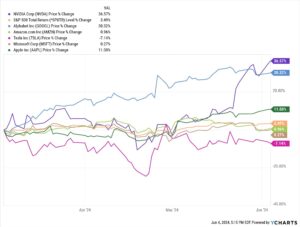
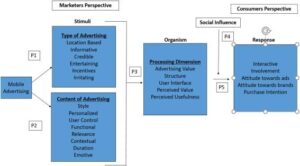
In recent years, artificial intelligence has reshaped industries and investment landscapes, with a select group of tech giants emerging as dominant forces in the AI revolution. Known as the “Magnificent 7,” these companies—Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Meta, Apple, Nvidia, and Tesla—have become synonymous with AI innovation and market leadership. As investors navigate the complex terrain of AI investments in 2024, understanding which of these technological powerhouses offers the most promising prospects has become increasingly crucial. This analysis explores the competitive positions, growth potential, and AI capabilities of these industry titans to identify the most compelling investment opportunity among the Magnificent 7. Water conservation practices have become increasingly vital in our modern world, where freshwater resources face mounting pressure from population growth, urbanization, and climate change. By implementing efficient water management strategies, both individuals and communities can significantly reduce their water footprint while maintaining quality of life and supporting environmental sustainability.
Indoor water conservation begins with simple yet effective measures in everyday household activities. Installing low-flow showerheads and faucet aerators can reduce water consumption by up to 50% without compromising performance. Dual-flush toilets offer different water volumes for liquid and solid waste, potentially saving thousands of gallons annually. Fixing leaky pipes and faucets prevents the waste of countless gallons of water that would otherwise drip away unnoticed.
The laundry room presents another opportunity for water savings. Modern washing machines with high-efficiency ratings use significantly less water than older models. Running full loads rather than partial ones maximizes the efficiency of each wash cycle. Cold water washing not only conserves energy but often cleans just as effectively as hot water for many types of laundry.
Outdoor water usage typically accounts for a substantial portion of household consumption, particularly in arid regions. Smart irrigation systems with moisture sensors ensure plants receive water only when needed, preventing overwatering and reducing waste. Choosing drought-resistant plants and native species that are well-adapted to local climate conditions naturally reduces irrigation requirements.
Rainwater harvesting systems capture and store precipitation for later use in gardens and landscapes. Simple rain barrels can collect roof runoff, while more sophisticated systems can supply water for multiple outdoor applications. This practice not only conserves municipal water supplies but also reduces stormwater runoff and associated pollution.
Commercial and industrial sectors can implement water-saving technologies such as water recycling systems, efficient cooling towers, and process optimization. Many industries have found that water conservation initiatives often lead to significant cost savings while improving their environmental performance and public image.
Agricultural water conservation employs techniques like drip irrigation, which delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff. Precision farming technologies use data analytics and sensors to optimize irrigation timing and volume, ensuring crops receive exactly what they need when they need it.
Community-wide initiatives play a crucial role in water conservation efforts. Public education programs raise awareness about water-saving practices and their importance. Water-efficient building codes and landscaping ordinances can mandate conservation measures in new construction and developments. Tiered water pricing structures encourage responsible usage by charging higher rates for excessive consumption.
Water quality protection goes hand in hand with conservation efforts. Preventing pollution, maintaining natural watersheds, and protecting groundwater sources ensures that available water resources remain usable. Treatment and recycling of wastewater can provide an additional source of water for non-potable uses, reducing demand on freshwater supplies.