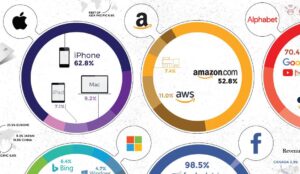
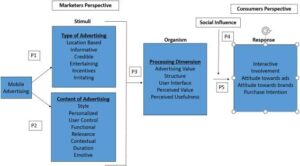
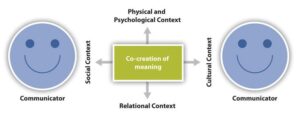
The artificial intelligence chip industry faces an unprecedented crisis as market valuations plummet by $1 trillion amid emerging technological disruptions. This dramatic downturn reflects growing concerns about new computing alternatives and shifting market dynamics that threaten traditional semiconductor manufacturers’ dominance in the AI sector. As established players grapple with evolving technological landscapes and increasing competition, the industry stands at a critical juncture that could reshape the future of AI hardware development. The intricate relationship between physical exercise and mental health has garnered significant attention from researchers and healthcare professionals worldwide. Regular physical activity triggers the release of endorphins, natural mood elevators that create feelings of happiness and euphoria. These chemical changes in the brain help reduce anxiety, depression, and negative mood while improving self-esteem and cognitive function.
Exercise promotes better sleep patterns by regulating the body’s circadian rhythm. Quality sleep is crucial for mental well-being, as it allows the brain to process emotional information and maintain emotional stability. When people engage in moderate to vigorous physical activity, they experience improved sleep quality and duration, leading to enhanced mental clarity and emotional resilience.
Physical activity also serves as a powerful stress management tool. During exercise, the body’s stress hormones, primarily cortisol and adrenaline, are reduced. This biological response helps individuals better cope with daily challenges and maintain emotional balance. Additionally, exercise provides a healthy outlet for frustration and anger, allowing people to channel negative emotions into productive physical activity.
The social aspects of exercise further contribute to mental wellness. Group activities, team sports, or even casual workout sessions with friends create opportunities for social interaction and support networks. These connections help combat feelings of isolation and loneliness, which are significant risk factors for mental health issues.
Regular physical activity enhances cognitive function by increasing blood flow to the brain and promoting neuroplasticity. This process facilitates the formation of new neural connections and strengthens existing ones, improving memory, concentration, and learning capabilities. Exercise also stimulates the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the survival of existing neurons and encourages the growth of new ones.
The mind-body connection strengthened through exercise extends beyond immediate benefits. Consistent physical activity helps build resilience against future mental health challenges by creating a foundation of healthy coping mechanisms. When individuals establish regular exercise routines, they develop discipline, goal-setting abilities, and a sense of accomplishment that transfers to other areas of life.
Different forms of exercise offer varied mental health benefits. While aerobic activities like running or cycling are excellent for reducing anxiety and depression, mindful exercises such as yoga or tai chi promote mental clarity and emotional balance. Strength training builds confidence and self-efficacy, while team sports develop social skills and cooperation.
The frequency and intensity of exercise needed for mental health benefits are surprisingly modest. Research indicates that even 30 minutes of moderate activity three times per week can significantly improve mental well-being. This accessibility makes exercise a practical and cost-effective approach to maintaining mental health, available to most individuals regardless of their fitness level or economic status.