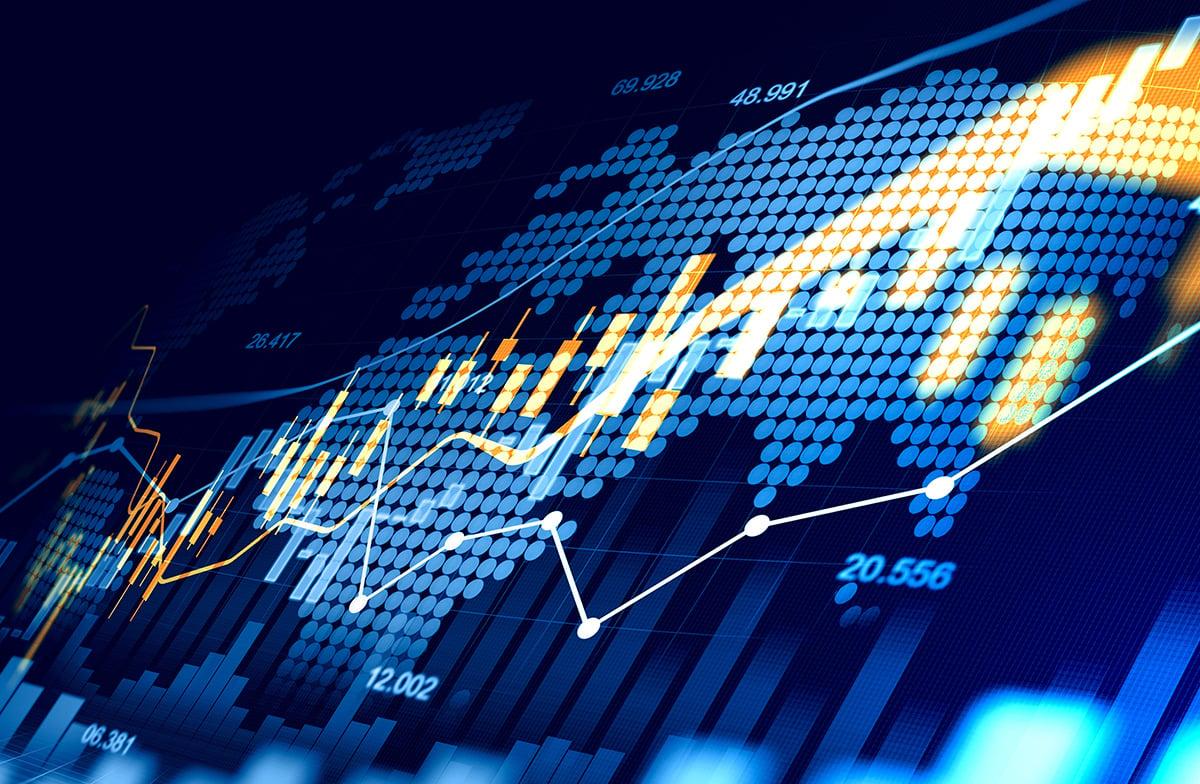
The technology sector’s dominant players, collectively known as the “Magnificent 7” – Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Nvidia, Meta, and Tesla – find themselves at a critical juncture in early 2024. After driving much of the stock market’s gains throughout 2023, these market leaders now confront shifting economic conditions, evolving regulatory landscapes, and changing investor sentiment. Their combined market capitalization and influence on major indexes has prompted both optimism and concern, raising questions about their ability to maintain momentum in an increasingly complex market environment. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, cybersecurity threats have become increasingly sophisticated, targeting individuals and organizations alike. Understanding these threats and implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting sensitive data and maintaining online safety.
Malware remains one of the most prevalent cyber threats, encompassing various malicious software types designed to infiltrate and damage computer systems. Ransomware attacks have seen a significant surge, encrypting victims’ files and demanding payment for their release. These attacks often target healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and government agencies, causing substantial financial losses and operational disruptions.
Phishing schemes have grown more intricate, utilizing social engineering tactics to deceive users into revealing confidential information. Cybercriminals now employ advanced techniques like spear-phishing, targeting specific individuals with personalized messages that appear legitimate. Multi-factor authentication and employee training programs have become essential in combating these threats.
Zero-day exploits pose a significant risk as they target previously unknown vulnerabilities in software applications. These attacks can remain undetected for extended periods, allowing attackers to harvest sensitive data or establish persistent access to compromised systems. Regular security updates and patch management are crucial defensive measures against such threats.
Supply chain attacks have emerged as a major concern, with cybercriminals targeting third-party vendors to gain access to larger organizations. These attacks exploit the trust relationships between businesses and their suppliers, highlighting the importance of thorough vendor security assessments and continuous monitoring.
Cloud security challenges have intensified as more organizations migrate their operations to cloud platforms. Misconfigured cloud settings, inadequate access controls, and data breaches through cloud services require comprehensive security strategies incorporating encryption, access management, and regular security audits.
Internet of Things (IoT) devices present unique security challenges due to their often limited security features and widespread deployment. Weak default passwords, lack of encryption, and infrequent security updates make IoT networks vulnerable to exploitation. Implementing network segmentation and robust device management policies helps mitigate these risks.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are being weaponized by threat actors to create more sophisticated attack vectors. These technologies enable automated attacks, intelligent malware that can evade detection, and advanced social engineering campaigns. Conversely, they also empower defensive capabilities through improved threat detection and response mechanisms.
Mobile devices face increasing threats through malicious applications, network attacks, and physical device compromises. The rise of remote work has expanded the attack surface, making mobile security essential for protecting corporate data accessed through personal devices.
State-sponsored cyber attacks continue to pose significant threats to national security and critical infrastructure. These sophisticated operations often involve advanced persistent threats (APTs) targeting specific organizations or sectors for espionage or disruption purposes. International cooperation and robust cybersecurity frameworks are vital for addressing these threats effectively.