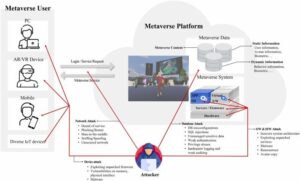
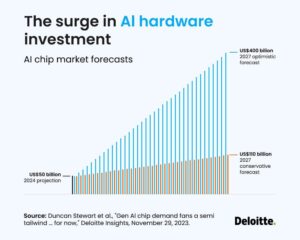
In recent years, a select group of technology companies has emerged as the dominant force driving Wall Street’s performance. Known as the “Magnificent Seven,” these tech giants – Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Nvidia, Meta, and Tesla - have collectively reshaped the investment landscape and significantly influenced market dynamics. Their combined market capitalization represents a substantial portion of the S&P 500, highlighting their outsized impact on the broader economy and financial markets. As these companies continue to innovate in areas ranging from artificial intelligence to cloud computing, their performance has become increasingly crucial for investors and market watchers alike. Virtual and augmented reality technologies have revolutionized the way we experience digital content, transforming various sectors from gaming to healthcare. These immersive technologies create distinct yet complementary experiences, each serving unique purposes and offering different levels of engagement with the digital world.
Virtual reality completely immerses users in a computer-generated environment, blocking out the physical world entirely. Through VR headsets, users step into artificial worlds where they can interact with digital objects and navigate synthetic spaces. This technology utilizes sophisticated tracking systems to monitor head movements and hand gestures, ensuring the virtual environment responds naturally to user actions.
Augmented reality, conversely, overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing rather than replacing physical reality. Users can view their surroundings through smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses while digital elements appear seamlessly integrated into their field of vision. This technology maps the physical environment and anchors virtual objects to specific locations, creating a mixed reality experience.
The applications of these technologies extend far beyond entertainment. In healthcare, surgeons use VR for training and planning complex procedures, while AR assists in visualizing patient data during actual operations. Educational institutions implement these tools to create interactive learning experiences, allowing students to explore historical sites, conduct virtual experiments, or examine 3D models of complex concepts.
The business sector has embraced these technologies for various purposes. Architects and designers use VR to walk clients through building proposals before construction begins. Retail companies employ AR to let customers virtually try on clothes or visualize furniture in their homes. Manufacturing facilities utilize AR for maintenance procedures, displaying step-by-step instructions overlaid on actual equipment.
Hardware requirements differ significantly between the two technologies. VR typically requires dedicated headsets with powerful processing capabilities and motion controllers. AR can function on everyday devices like smartphones, though specialized AR glasses offer more sophisticated experiences. Both technologies continue to evolve, with improvements in resolution, field of view, and tracking accuracy.
The future holds promising developments for both VR and AR. Mixed reality experiences, combining elements of both technologies, are becoming more prevalent. Advances in haptic feedback systems will enhance the sense of touch in virtual environments. Miniaturization of components may lead to more comfortable and portable devices, while improvements in processing power will enable more realistic and complex digital interactions.
Network infrastructure plays a crucial role in the advancement of these technologies. The implementation of 5G networks enables faster data transmission and reduced latency, essential for seamless AR experiences and cloud-based VR applications. This connectivity enhancement opens new possibilities for remote collaboration and shared virtual experiences across vast distances.