In the ever-evolving landscape of global technology, FAANG+ companies – Facebook (now Meta), Amazon, Apple, Netflix, Google (Alphabet), and other tech giants – have emerged as dominant forces shaping our digital future. These market leaders, with their combined market capitalization exceeding several trillion dollars, represent more than mere corporate success stories; they embody the technological revolution of the 21st century. From social media and e-commerce to streaming services and cloud computing, these companies have fundamentally transformed how we live, work, and interact. This deep dive examines their business models, market influence, and the factors that have propelled them to their current positions of prominence in the global economy. Virtual reality (VR) technology has revolutionized the way we experience digital content, transforming various industries and creating immersive experiences that were once confined to science fiction. By combining sophisticated hardware with advanced software solutions, VR systems enable users to step into computer-generated environments that simulate real-world scenarios or create entirely new realms of possibility.
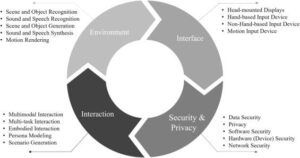
The fundamental components of VR systems include head-mounted displays (HMDs), motion sensors, and controllers that work together to create a seamless interactive experience. These devices track user movements and translate them into corresponding actions within the virtual environment, providing a natural and intuitive interface for interaction.
Applications of VR technology extend far beyond gaming and entertainment. In healthcare, medical professionals use VR for surgical training and planning complex procedures without risk to actual patients. Educational institutions implement VR to create engaging learning environments, allowing students to explore historical sites, conduct virtual experiments, or practice specialized skills in a safe, controlled setting.
The architecture and real estate sectors have embraced VR for virtual property tours and design visualization, enabling clients to experience spaces before they are built. This capability significantly reduces costs and time associated with physical mockups while facilitating better decision-making during the design process.
Manufacturing industries utilize VR for product design, assembly planning, and worker training. Engineers can evaluate prototypes virtually, identify potential issues early in the development cycle, and optimize production processes before implementation. This approach minimizes expensive physical prototyping and accelerates time-to-market for new products.
The psychological applications of VR have shown promising results in treating phobias, anxiety disorders, and PTSD through exposure therapy. Patients can confront their fears in a controlled environment while therapists monitor and adjust the intensity of the experience to ensure optimal therapeutic outcomes.
As telecommunications evolve, VR platforms are emerging as powerful tools for remote collaboration and social interaction. Virtual meeting spaces allow participants to interact naturally, share documents, and work on projects together, regardless of their physical location. This capability has become particularly relevant in the era of remote work and global teams.
The future of VR technology holds even more potential as hardware becomes more sophisticated and affordable. Advances in haptic feedback systems will enable users to feel virtual objects, while improvements in display technology will deliver more realistic visual experiences. Integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning will create more responsive and personalized virtual environments.
The development of wireless VR systems and reduced form factors will make the technology more accessible and convenient for everyday use. As 5G networks become widespread, cloud-based VR experiences will become more prevalent, eliminating the need for powerful local processing hardware and expanding the possibilities for mobile VR applications.