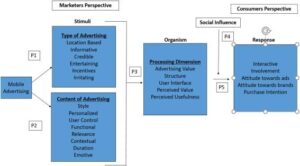
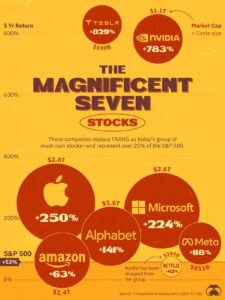
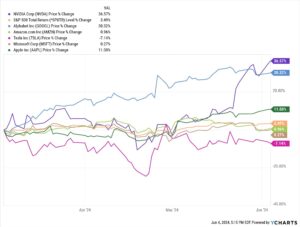
The technology industry landscape is undergoing a significant shift as Microsoft positions itself to challenge Apple’s market dominance, following its successful strategic alignment with NVIDIA in the artificial intelligence sector. This realignment of tech powers comes at a time when AI capabilities are increasingly defining corporate valuations and market influence, marking a potential changing of the guard in Silicon Valley’s traditional hierarchy. The transformation reflects broader changes in how technology companies are valued, with AI capabilities now rivaling consumer products as a key metric of corporate strength. The evolution of artificial intelligence has sparked both excitement and concern across various sectors of society. While some herald AI as a revolutionary force for positive change, others express deep reservations about its potential implications. This technology has already transformed numerous industries, from healthcare and finance to transportation and entertainment, fundamentally altering how we work, live, and interact.
AI systems now perform complex medical diagnoses, predict market trends, operate autonomous vehicles, and create sophisticated artistic works. These applications demonstrate the technology’s versatility and its capacity to enhance human capabilities rather than simply replace them. Machine learning algorithms continue to improve, becoming increasingly adept at pattern recognition and decision-making processes that once seemed exclusively human domains.
However, the rapid advancement of AI technology raises important ethical considerations. Questions about data privacy, algorithmic bias, and the potential displacement of human workers demand careful attention. The collection and utilization of vast amounts of personal data to train AI systems have prompted discussions about consent and individual privacy rights. Similarly, instances of AI systems exhibiting biased behavior have highlighted the need for diverse development teams and robust testing protocols.
The economic impact of AI adoption varies across different sectors and regions. While some industries experience increased productivity and efficiency, others face significant workforce disruption. This technological transition requires careful management to ensure equitable distribution of benefits and appropriate support for affected workers. Education and training programs must evolve to prepare current and future generations for an AI-integrated workplace.
Research continues to push the boundaries of AI capabilities, exploring areas such as natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. These developments suggest future applications that could range from more sophisticated personal assistants to advanced problem-solving systems capable of addressing complex global challenges. The potential for AI to contribute to scientific discovery, environmental protection, and social progress remains largely untapped.
Regulatory frameworks are gradually emerging to govern AI development and deployment. These policies aim to balance innovation with safety and ethical considerations, ensuring responsible advancement of the technology. International cooperation becomes increasingly important as AI systems cross national boundaries and affect global markets and societies.
Critics and proponents alike acknowledge the need for thoughtful discourse about AI’s role in society. The technology’s impact extends beyond technical capabilities to fundamental questions about human identity, creativity, and purpose. As AI systems become more sophisticated, society must grapple with philosophical and practical questions about consciousness, intelligence, and the nature of human-machine interaction.
The integration of AI into daily life continues steadily, despite ongoing debates about its implications. This transformation requires careful consideration of both opportunities and challenges, ensuring that technological progress serves human interests while mitigating potential risks.