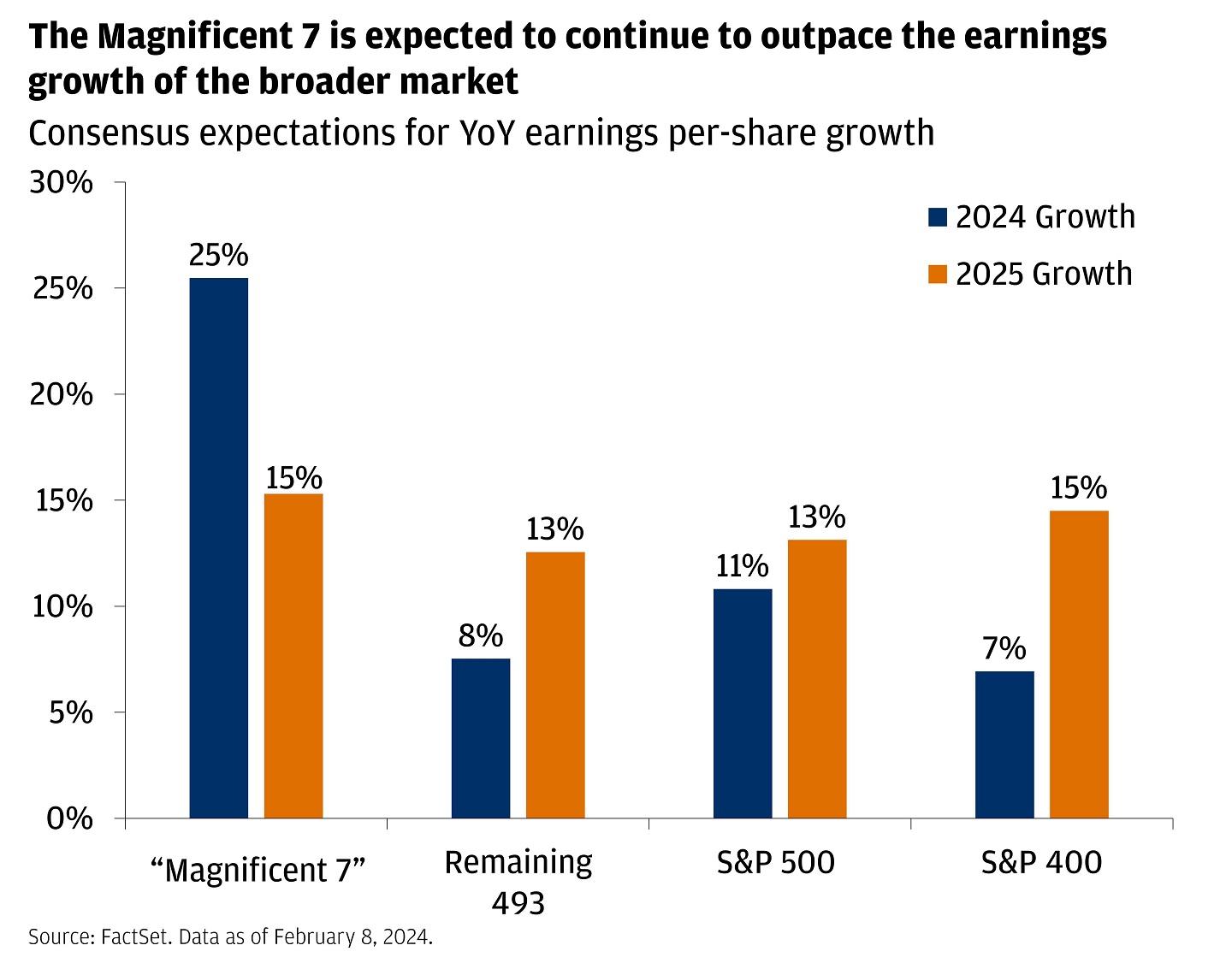
The stock market’s robust performance in early 2024 has been notably concentrated, with major technology companies emerging as the primary drivers of the S&P 500’s upward trajectory. Just a handful of tech giants, including Microsoft, Apple, Nvidia, Meta, and Amazon, have contributed to more than half of the index’s gains, highlighting both the growing influence of technology sector and the increasingly top-heavy nature of market returns. This concentration of gains among select tech companies raises important questions about market breadth and the sustainability of the current rally. Virtual reality technology has revolutionized the way we experience digital content, offering immersive experiences that blur the lines between real and virtual worlds. As this technology continues to evolve, it presents both opportunities and challenges for various industries, from gaming and entertainment to healthcare and education.
The fundamental principle behind VR involves creating a three-dimensional, computer-generated environment that users can interact with through specialized hardware. Head-mounted displays (HMDs) track user movements and adjust the visual perspective accordingly, while motion controllers enable natural interaction with virtual objects. Advanced systems incorporate haptic feedback, providing tactile sensations that enhance the sense of presence.
Educational institutions have embraced VR as a powerful teaching tool, allowing students to explore historical sites, conduct virtual dissections, or practice complex procedures without risk. Medical professionals use VR simulations for surgical training and planning, while architects and engineers utilize it for design visualization and collaboration.
The gaming industry has particularly benefited from VR advancement, with dedicated platforms and titles offering unprecedented levels of immersion. Players can physically dodge attacks, aim weapons naturally, and experience environments from a first-person perspective. Social VR platforms enable users to interact with others in virtual spaces, fostering new forms of digital communication and community building.
However, technical limitations persist. Current VR systems often struggle with resolution, field of view, and motion sickness issues. The “screen door effect,” where users can distinguish individual pixels, remains a challenge for display technology. Wireless solutions face bandwidth constraints, while tethered systems restrict movement.
Cost considerations also impact widespread adoption. High-quality VR systems require significant investment in hardware and computing power. Content creation for VR is more complex and expensive than traditional media, leading to limited available experiences.
Privacy and security concerns emerge as VR systems collect extensive user data, including movement patterns and physical responses. The potential for misuse of this information raises questions about data protection and user rights in virtual environments.
Research continues into improving VR technology through advanced optics, increased processing power, and enhanced tracking systems. Emerging technologies like eye-tracking and brain-computer interfaces promise more natural interaction methods. Miniaturization efforts aim to create more comfortable and portable devices.
The therapeutic applications of VR show promising results in treating phobias, PTSD, and chronic pain. Virtual exposure therapy allows controlled confrontation of fears, while distraction-based applications help manage pain during medical procedures.
As VR technology matures, its impact extends beyond entertainment into professional training, remote collaboration, and therapeutic applications. The convergence with other technologies, such as artificial intelligence and 5G networks, suggests future developments that could further transform how we interact with digital content and each other in virtual spaces.