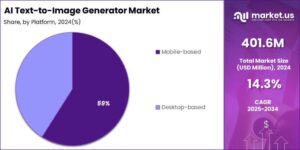
The technology sector’s landscape continues to be dominated by a handful of major players, and industry analysts predict this trend will likely persist through 2025. Companies like Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet, and Meta have not only maintained their market leadership but are actively expanding into emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and mixed reality. Their substantial financial resources, established infrastructure, and extensive user bases provide these tech giants with significant advantages over potential competitors, raising questions about market competition and innovation in the coming years. The intricate relationship between genetics and environmental factors shapes our physical characteristics, personality traits, and overall health outcomes. While DNA serves as the blueprint for life, external influences play a crucial role in determining how these genetic instructions are expressed.
Genetic inheritance follows complex patterns, with genes being passed down from parents to offspring through chromosomes. These genetic sequences contain instructions for producing proteins that control various biological processes. However, the presence of specific genes doesn’t guarantee their expression, as environmental factors can activate or suppress genetic activity through epigenetic modifications.
Research has shown that lifestyle choices significantly impact gene expression. Diet, exercise, stress levels, and exposure to toxins can alter how genes function without changing the underlying DNA sequence. For instance, identical twins with the same genetic makeup may develop different health conditions based on their individual lifestyle choices and environmental exposures.
The concept of gene-environment interaction explains why some individuals with genetic predispositions to certain conditions may never develop them, while others without apparent genetic risk factors do. This interaction is particularly evident in complex traits and diseases, where multiple genes and environmental factors contribute to the final outcome.
Early life experiences can have lasting effects on gene expression through epigenetic modifications. Childhood trauma, nutrition, and exposure to environmental pollutants can influence how genes are expressed throughout life. These modifications can even be passed down to future generations, although the changes themselves are not permanent alterations to the DNA sequence.
Scientists have identified specific mechanisms through which environmental factors influence gene expression. DNA methylation, histone modifications, and RNA interference are some of the primary epigenetic processes that regulate gene activity in response to environmental signals. These mechanisms can either enhance or suppress gene expression, leading to variations in physical traits and disease susceptibility.
Understanding the relationship between genetics and environment has practical applications in healthcare and disease prevention. By recognizing how lifestyle choices affect gene expression, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize their health outcomes. Healthcare providers can develop personalized treatment plans that consider both genetic predispositions and environmental factors.
Advances in genetic research continue to reveal new insights into this complex interaction. The field of nutrigenomics examines how different nutrients affect gene expression, while environmental epigenetics studies the impact of various environmental exposures on genetic function. These discoveries are reshaping our understanding of human development and disease progression.
Recent studies have highlighted the importance of timing in gene-environment interactions. Certain environmental factors may have stronger effects during specific developmental stages or life phases. This knowledge has implications for preventive medicine and public health strategies, suggesting that interventions may be most effective when targeted at critical periods of development.