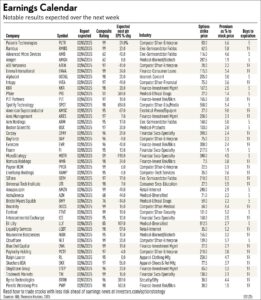
The tech sector’s dominance in global markets has been particularly evident through the performance of the Magnificent Seven – Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, Nvidia, Meta, and Tesla. These technology giants have shaped market dynamics throughout 2024, collectively influencing major stock indices and demonstrating remarkable resilience amid economic uncertainties. This analysis examines their individual and collective performance, market capitalization shifts, and key strategic moves that defined their trajectories during the year. The intricate dance between soil health and agricultural productivity forms the cornerstone of sustainable farming practices. Farmers worldwide increasingly recognize that maintaining optimal soil conditions directly impacts crop yields, resource efficiency, and long-term environmental sustainability. Key factors like organic matter content, nutrient availability, and microbial activity play crucial roles in determining soil quality.
Implementing proper soil management techniques begins with regular testing to assess pH levels, nutrient content, and structural composition. This scientific approach enables farmers to make informed decisions about amendments and fertilization strategies. Cover cropping, crop rotation, and minimal tillage practices help preserve soil structure while preventing erosion and nutrient leaching.
Organic matter serves as the foundation for healthy soil ecosystems. It improves water retention, enhances nutrient cycling, and provides essential food sources for beneficial microorganisms. Incorporating crop residues, compost, and green manures can significantly boost organic matter levels over time. These additions create a more resilient soil system capable of supporting robust plant growth while reducing the need for synthetic inputs.
Modern farming operations increasingly utilize precision agriculture technologies to optimize soil management. GPS-guided equipment and soil mapping tools enable variable-rate application of nutrients and amendments, ensuring resources are allocated efficiently across fields. This targeted approach minimizes waste while maximizing the benefits of inputs applied to specific areas requiring attention.
The soil food web, comprising countless microscopic organisms, performs vital functions in nutrient cycling and disease suppression. Beneficial bacteria and fungi form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake and protecting against pathogens. Managing soil biology through reduced pesticide use and appropriate organic matter additions helps maintain these beneficial relationships.
Climate change considerations have brought renewed focus to soil’s role in carbon sequestration. Implementing practices that build soil organic carbon not only improves agricultural productivity but also contributes to climate change mitigation efforts. No-till farming, perennial cropping systems, and integrated livestock management can significantly increase soil carbon storage capacity.
Water management becomes increasingly critical as climate patterns shift and resources become scarcer. Healthy soils with good structure and organic matter content naturally retain more moisture, reducing irrigation requirements and improving drought resilience. Proper drainage and erosion control measures protect these valuable soil resources from degradation during extreme weather events.
Successful soil management requires a long-term perspective and commitment to sustainable practices. While some improvements may take years to manifest, the cumulative benefits of enhanced soil health include reduced input costs, improved crop quality, and greater farm resilience. Farmers who prioritize soil health position themselves for success in an evolving agricultural landscape while contributing to environmental conservation efforts.