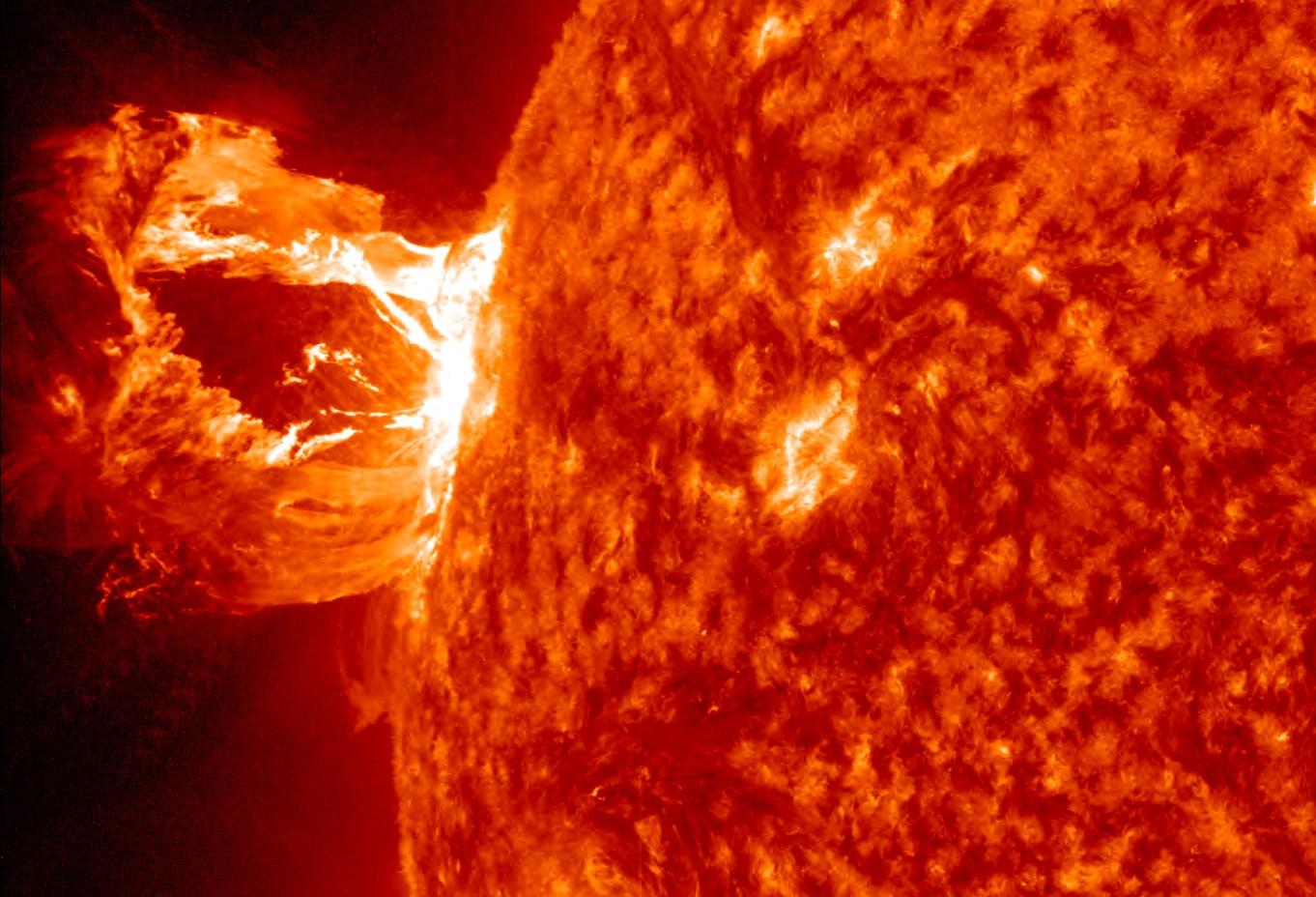
Solar storms, powerful bursts of electromagnetic energy from the Sun, are causing widespread disruptions to agricultural operations across multiple regions today. Modern farming equipment, heavily dependent on GPS systems and electronic controls, has experienced unexpected failures and navigation errors due to the intense solar activity. These geomagnetic disturbances, while common in space weather patterns, rarely affect ground-level technology with such severity. The current solar event has particularly impacted precision agriculture systems, automated tractors, and irrigation controls, forcing many farmers to temporarily revert to manual operations. Recent reports from agricultural regions across multiple states indicate widespread disruption of GPS-guided farming equipment due to intense solar activity. Farmers operating modern tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems have experienced unexpected shutdowns and navigation errors, leading to significant delays in crucial farming operations.
The geomagnetic disturbance, caused by a massive coronal mass ejection from the sun, has particularly affected precision agriculture systems that rely heavily on satellite connectivity. Equipment manufacturers have confirmed that the solar interference is disrupting signals between farming machinery and positioning satellites, rendering autonomous features temporarily unreliable.
Several large-scale farming operations in the Midwest reported their autonomous tractors veering off predetermined paths, while others experienced complete system failures. The sophisticated technology that typically ensures precise seed placement and optimized fertilizer distribution has become increasingly unstable, forcing many farmers to revert to manual operation methods.
Agricultural technology experts explain that modern farming equipment depends on intricate networks of sensors and satellite communications to maintain accuracy within centimeters. When solar storms interfere with these systems, the resulting electromagnetic interference can cause positioning errors of several meters, making automated farming operations impossible.
The National Weather Service’s Space Weather Prediction Center has issued alerts about continued solar activity expected to persist for the next 48-72 hours. This timeline is particularly concerning for farmers in the midst of critical planting or harvesting periods, as delays could significantly impact crop yields and operational costs.
Equipment manufacturers have begun pushing emergency software updates to help stabilize affected systems, but these measures provide only partial protection against the intense solar activity. Technical support hotlines are experiencing unprecedented call volumes as farmers seek solutions to keep their operations running.
Insurance companies are currently assessing whether damages and losses resulting from solar-storm-related equipment malfunctions will be covered under existing agricultural insurance policies. This situation has sparked discussions about the need for specific coverage addressing technological vulnerabilities in modern farming operations.
The current disruptions highlight the delicate balance between technological advancement and environmental factors in contemporary agriculture. While precision farming technologies have revolutionized agricultural efficiency, their susceptibility to solar events reveals potential vulnerabilities in the food production system.
Agricultural economists estimate that each day of disrupted operations could cost larger farming operations thousands of dollars in lost productivity and potential crop damage. Smaller farms, operating with tighter margins, face particularly challenging decisions about whether to pause operations or risk continuing with compromised equipment.
Weather monitoring stations and agricultural research centers are actively collecting data on these disruptions, aiming to develop more resilient systems for future implementation. This event serves as a crucial case study for designing next-generation farming equipment with enhanced protection against solar interference.