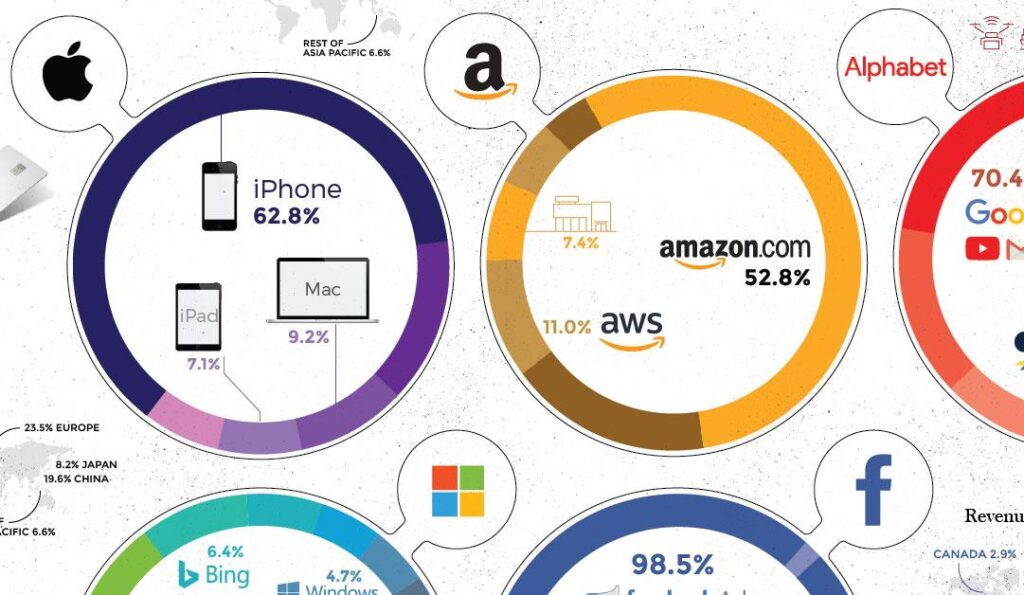
Tech giants stand at a pivotal moment as Q1 earnings season approaches, with investors and market watchers closely monitoring their performance amid ongoing economic uncertainties. These technology behemoths, including Apple, Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, and Meta, have faced various challenges and opportunities in recent months, from AI advancements to regulatory scrutiny. Understanding their current position and key metrics before earnings announcements can provide crucial context for what’s to come in the technology sector. Sustainable agriculture practices have become increasingly vital in today’s world, where environmental concerns intersect with food security needs. These methods focus on maintaining ecological balance while ensuring profitable farming and healthy communities. Farmers worldwide are adopting techniques that preserve natural resources, enhance soil fertility, and promote biodiversity.
Cover cropping stands out as a fundamental practice, where farmers plant specific crops between growing seasons to protect and enrich the soil. These crops prevent erosion, suppress weeds, and add valuable organic matter when tilled back into the ground. Leguminous cover crops, such as clover and vetch, naturally fix nitrogen in the soil, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Crop rotation plays a crucial role in sustainable farming by breaking pest and disease cycles while maintaining soil health. This systematic approach involves growing different crops in sequence on the same plot. For instance, following corn with soybeans helps manage nutrient levels and reduces the buildup of crop-specific pests.
Water conservation techniques have evolved significantly, with precision irrigation systems leading the way. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing waste through evaporation and runoff. Soil moisture sensors and weather monitoring systems help farmers optimize water usage based on actual crop needs.
Integrated pest management (IPM) represents another cornerstone of sustainable agriculture. This approach combines biological controls, habitat manipulation, and resistant plant varieties to manage pests with minimal chemical intervention. Beneficial insects are encouraged through habitat preservation, while cultural practices help prevent pest problems before they begin.
Composting and organic matter management contribute significantly to soil health. Farmers create nutrient-rich compost from agricultural waste, food scraps, and plant materials. This natural fertilizer improves soil structure, enhances water retention, and supports beneficial soil microorganisms.
Modern sustainable practices also incorporate precision farming technologies. GPS-guided equipment reduces overlap in field operations, saving fuel and minimizing soil compaction. Satellite imagery and drone monitoring help farmers identify crop stress and nutrient deficiencies early, enabling targeted interventions.
Agroforestry systems combine trees with crops or livestock, creating diverse, productive landscapes. These systems provide multiple benefits, including improved soil stability, enhanced biodiversity, and additional income streams through tree products.
Conservation tillage methods minimize soil disturbance, protecting soil structure and reducing erosion. No-till farming leaves crop residue on the field surface, building organic matter and supporting soil life. This approach also helps sequester carbon, contributing to climate change mitigation.
Animal integration in farming systems creates synergistic relationships. Rotational grazing improves pasture health while providing natural fertilization. Animals help manage crop residues and contribute to farm diversity, making the entire system more resilient and sustainable.
These practices work together to create farming systems that are environmentally sound, economically viable, and socially responsible. As climate challenges intensify and population growth continues, sustainable agriculture becomes increasingly crucial for global food security and environmental protection.