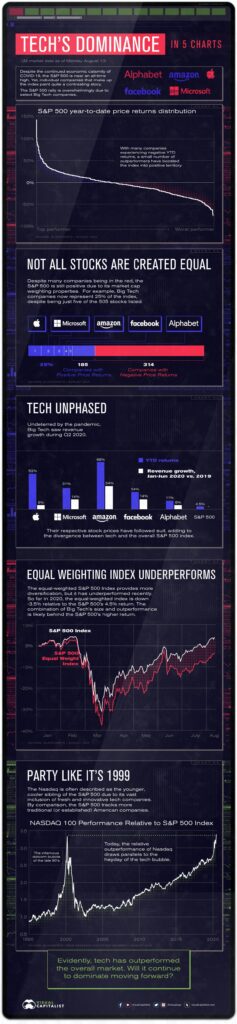
The dominance of technology megacaps in global markets has become one of the most significant economic phenomena of the 21st century. As investors and analysts track the growing influence of these tech giants, their combined market capitalization has reached unprecedented levels, reshaping traditional market dynamics. This visualization breaks down the market share distribution among leading technology companies, illustrating how a select few corporations have come to command an outsized portion of total market value. In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses constantly seek innovative ways to streamline their operations and enhance efficiency. Cloud computing has emerged as a transformative solution, revolutionizing how organizations store, manage, and process data. This technology enables companies to access computing resources, applications, and services through the internet, eliminating the need for extensive physical infrastructure.
The fundamental principle behind cloud computing lies in its ability to provide scalable, on-demand resources. Organizations can adjust their computing capacity based on their requirements, paying only for what they use. This flexibility proves particularly beneficial for businesses experiencing fluctuating demands or seasonal peaks in their operations.
Cloud services typically fall into three main categories: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing businesses to rent servers, storage, and networking components. PaaS offers a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications, while SaaS delivers software applications directly through web browsers.
Security remains a paramount concern in cloud computing. Service providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, authentication protocols, and regular security updates. Many cloud platforms offer advanced threat detection and prevention capabilities, often surpassing the security measures small to medium-sized businesses could implement independently.
Data backup and disaster recovery become more manageable with cloud computing. Organizations can automatically backup their data to multiple locations, ensuring business continuity in case of system failures or natural disasters. This redundancy provides peace of mind and reduces the risk of data loss.
Cost efficiency represents another significant advantage. By migrating to the cloud, businesses eliminate substantial capital expenditure on hardware and reduce ongoing maintenance costs. The pay-as-you-go model allows for better budget allocation and financial planning.
Collaboration and accessibility improve dramatically through cloud computing. Team members can access files and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and global operations. Real-time collaboration tools enable multiple users to work simultaneously on projects, enhancing productivity and reducing time-to-market.
Environmental sustainability benefits from cloud adoption as well. Shared resources and optimized data centers result in lower energy consumption compared to individual organizations maintaining their own IT infrastructure. This reduction in carbon footprint aligns with growing environmental consciousness in business operations.
Integration capabilities extend the functionality of cloud services. APIs and middleware solutions enable seamless connection between different applications and services, creating a cohesive digital ecosystem. This interoperability supports automation and workflow optimization across various business processes.
Modern cloud platforms also incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities, enabling organizations to analyze vast amounts of data and derive actionable insights. These advanced features support better decision-making and help identify new business opportunities or operational inefficiencies.