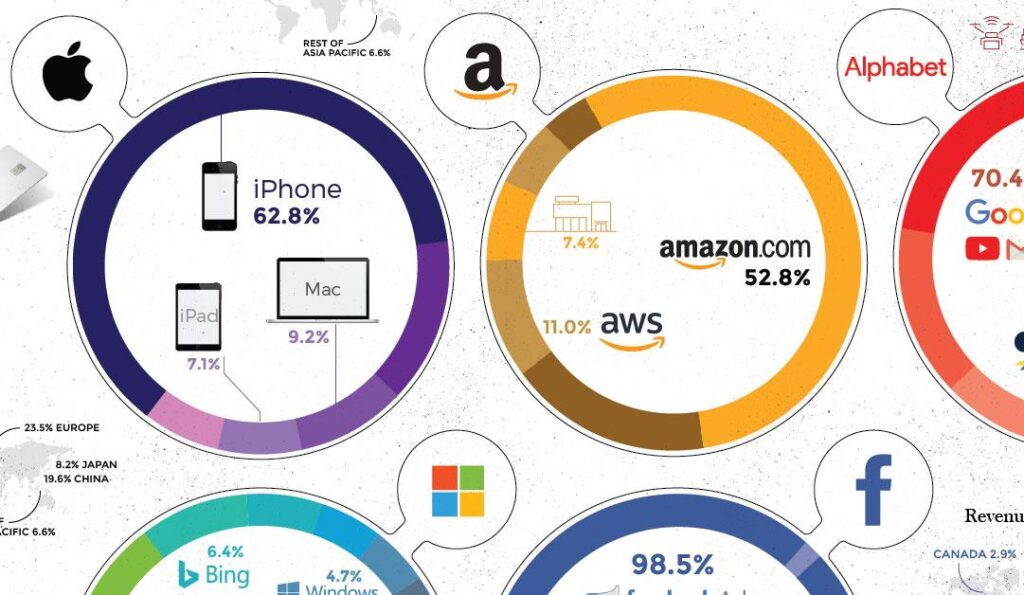
In today’s financial landscape, technology companies have emerged as the dominant force on Wall Street, wielding unprecedented market influence and shaping global economic trends. These tech titans, through their innovative products, services, and business models, have not only transformed how we live and work but have also become the cornerstone of modern investment portfolios. As these industry leaders continue to push boundaries and maintain their stronghold on market valuations, understanding their position and impact on Wall Street has become essential for investors and market observers alike. This article examines seven of the most influential tech companies that currently dominate the stock market, exploring their market presence and the factors behind their continued success. The evolution of digital technology has fundamentally transformed how businesses operate and interact with their customers. Cloud computing represents a cornerstone of this transformation, enabling organizations to access computing resources, storage, and applications through the internet instead of maintaining physical infrastructure.
Cloud computing offers three primary service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, allowing businesses to rent servers, storage, and networking components. PaaS delivers a platform that enables developers to build, test, and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance.
Organizations benefit from cloud computing through enhanced scalability, cost efficiency, and operational flexibility. The pay-as-you-go model eliminates large upfront investments in hardware and software, while automatic updates ensure systems remain current without manual intervention. Cloud solutions facilitate remote work capabilities, enabling employees to access necessary resources from anywhere with an internet connection.
Security considerations in cloud computing involve data protection, compliance requirements, and access control. Cloud service providers implement robust security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and regular security audits. Organizations must understand their responsibilities within the shared security model and implement appropriate controls to protect sensitive information.
Data migration and integration present challenges when adopting cloud solutions. Organizations must carefully plan the transfer of existing data and applications to cloud environments while maintaining business continuity. Integration between cloud-based and on-premises systems requires careful consideration of compatibility and data synchronization.
Performance optimization in cloud environments involves monitoring resource utilization, implementing caching strategies, and selecting appropriate instance types. Organizations must balance cost considerations with performance requirements to achieve optimal results. Auto-scaling capabilities allow systems to automatically adjust resources based on demand, ensuring consistent performance during peak usage periods.
Disaster recovery and business continuity planning become more streamlined with cloud computing. Geographic distribution of data centers provides redundancy, while automated backup and recovery processes reduce downtime risks. Cloud providers offer various tools and services to implement comprehensive disaster recovery strategies.
The future of cloud computing points toward increased adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud approaches, allowing organizations to leverage different providers and services based on specific requirements. Edge computing complements cloud services by processing data closer to its source, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities continue to expand within cloud platforms, enabling advanced analytics and automation capabilities.
Environmental considerations include the energy efficiency of data centers and the reduction of physical infrastructure requirements. Cloud providers increasingly invest in renewable energy sources and implement efficient cooling systems to minimize environmental impact.